
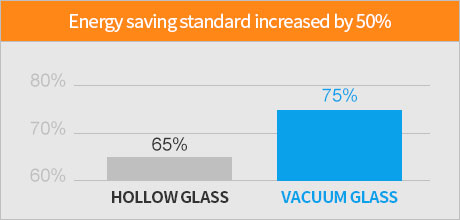
·Residential buildings in Hebei, Tianjin, Shandong and other provinces have all started to implement 75% energy-saving standards.
·Since January 1, 2021, all residential buildings in Beijing have started to implement the 80% energy-saving standard (requiring the K value of the whole window to be less than 1.1w/(m2.k)).

China's new building area is 2 billion ㎡ every year, of which 80%-90% do not meet the international energy-saving standards.
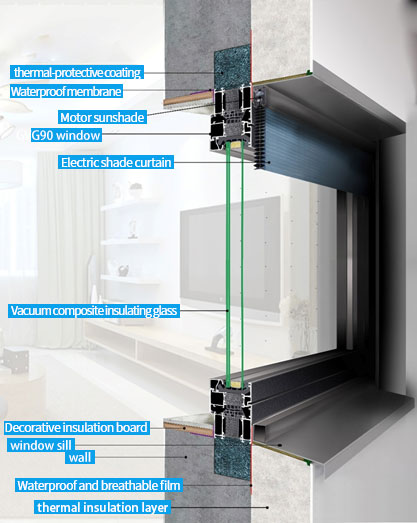
The carbon emission in the use stage accounts for 22% of the national total, and the energy loss through windows accounts for more than 50% of the energy consumption in use. Therefore, improving the thermal insulation performance of windows is the most direct way to prevent the heat loss of buildings.
In order to achieve the double-carbon goal, it has become the primary task of governments at all levels to vigorously develop ultra-low energy consumption buildings and near-zero energy consumption buildings. As the new generation of the most energy-saving glass, vacuum glass will inevitably usher in a huge development opportunity.
The market size of energy-saving glass exceeds 200 billion, and the demand is 400 million ㎡/year.
The new market
It is estimated that by 2023, 100 million ㎡ of ultra-low energy consumption buildings will be started in China, and the market demand for vacuum glass will exceed 20 million ㎡, with a market size of over 10 billion yuan.
After the 14th Five-Year Plan, there will be more than 200 million ㎡ energy-saving glass demand in the new building market every year, and the market scale will exceed 100 billion.
Stock market
China's stock of buildings exceeds 46 billion ㎡. In the next decade, more than 11 billion ㎡ of buildings will need to replace high-performance energy-saving doors and windows, and there will be more than 200 million ㎡ of energy-saving glass every year. After the renovation, 420 million tons of coal will be saved.